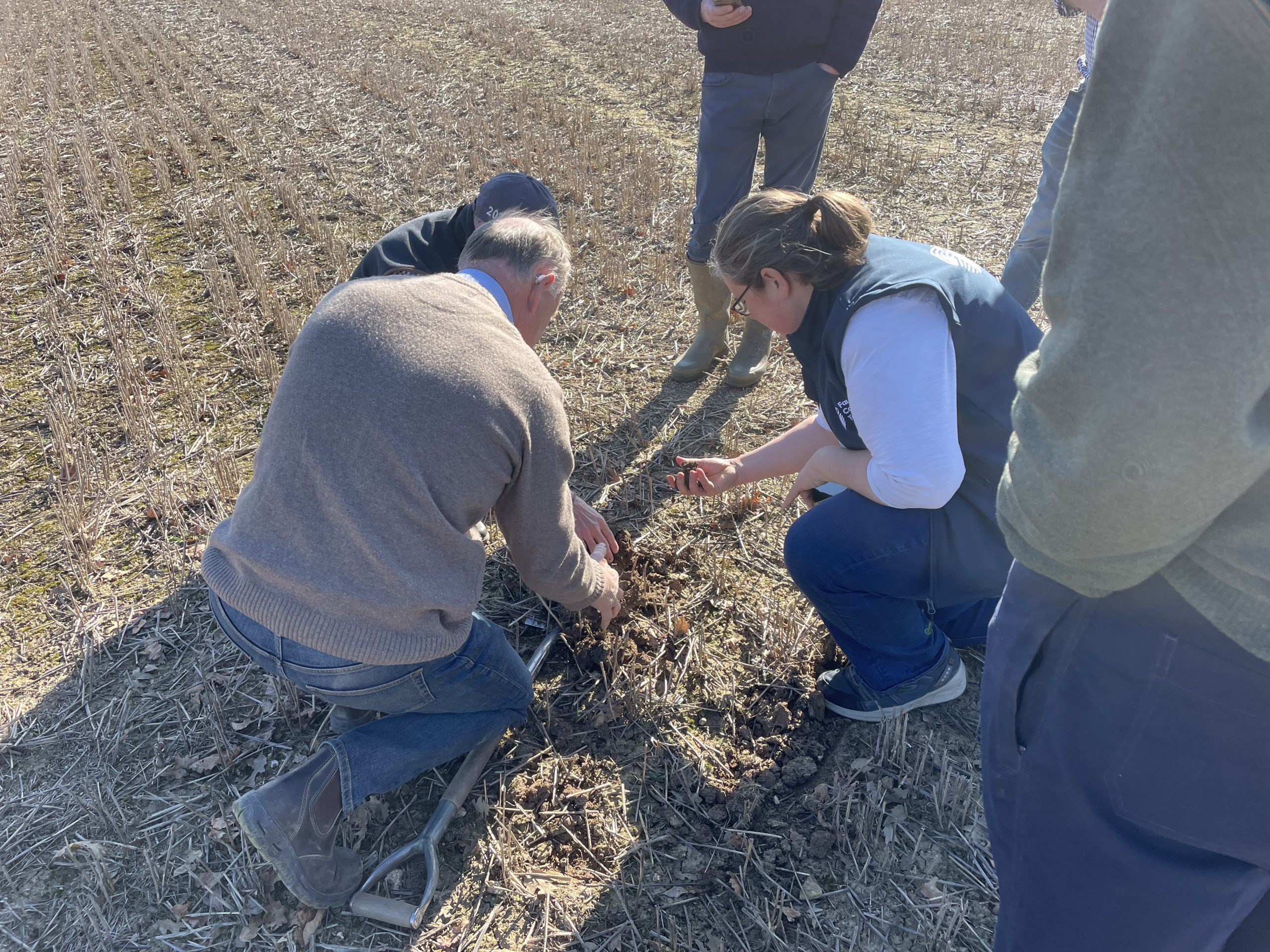

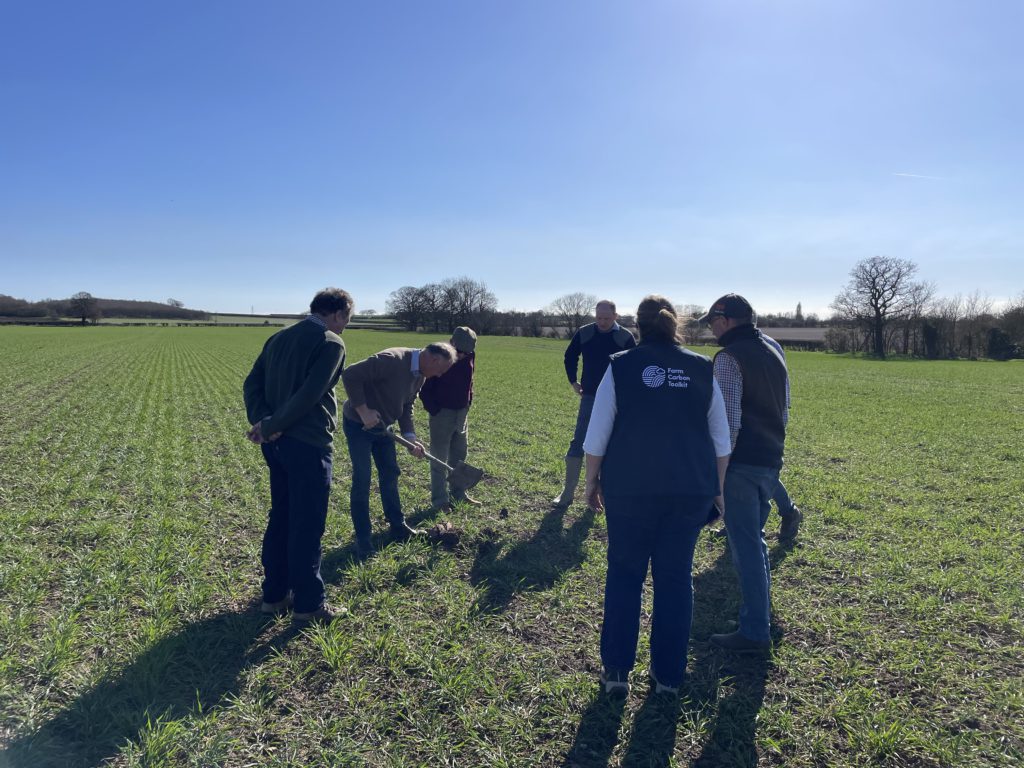
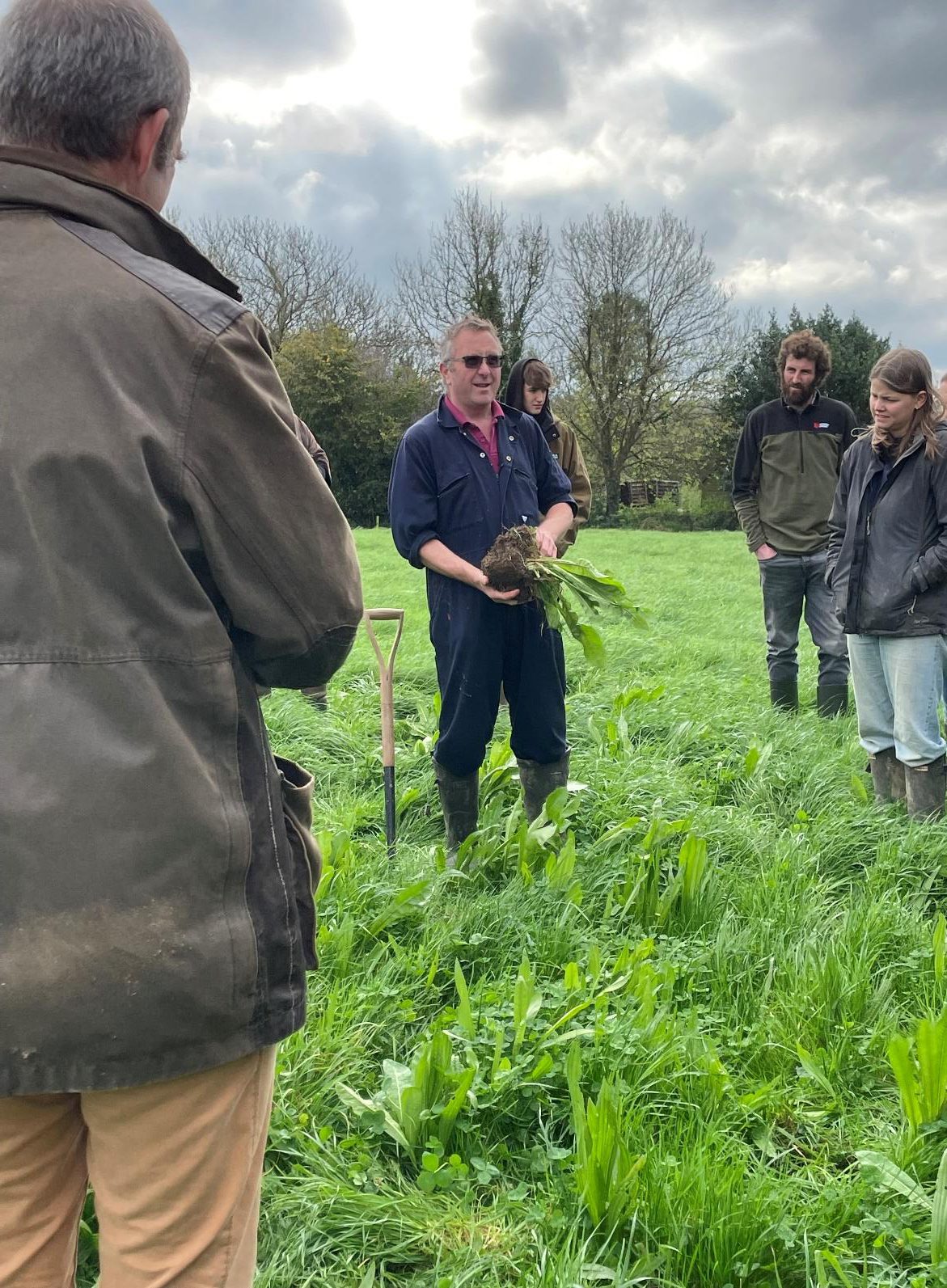
On a sunny day at the end of March, farmers gathered with Simon Cowell to take part in a farm walk with our Soil Farmer of the Year Winner from 2018. Thanks to funding from the AFN+ network, we have been able to revisit two farms this year to understand how their farm and management systems have evolved since being awarded.
Simon farms 400 acres of heavy clay with a large acreage below sea level. He has been working on improving his soils for the last 25 years, and moved to a no-till system in 2006, being flexible with both management and rotations to prioritise soil health.
Originally starting as a dairy farm, Simon converted his farm to arable cropping. At that time, it was full cultivation and deep topsoil ploughing, year after year. For 15 to 20 years, it seemed to work. But then something shifted — yields dropped, costs rose, and the soil stopped cooperating, as Simon reflects here:
“The farm is on heavy clay with high magnesium content. It became impossible to make a workable seedbed. The soil was either too wet and smeared or too dry and baked hard. I’d tried gypsum, but nothing made a lasting difference. Eventually, it became obvious: the more I left the soil alone, the better it behaved.”
During the walk, lots of different topics were discussed — from rotations, cultivation choice, to measuring soil health and the value of organic matter. Below, Simon shares some of his reflections on how his management has evolved over the last 25 years:
Direct Drilling
In 2004, Simon bought his first direct drill and hasn’t looked back since. Establishing crops became more reliable and consistent, especially on the heavy land.
He uses two drills — a disc and a tine drill. The Moore disc drill is brilliant when conditions are right but struggles in extremes (too wet or too dry). The tine drill, on the other hand, works in almost anything. He will often alternate depending on soil conditions, and finds that flexibility is incredibly important to meet the different challenges that may occur.
Building Soil Organic Matter — and Balancing It
Simon reflects:
“One of the biggest long-term wins has been improving soil organic matter. After years of minimal disturbance, my soil tests show I’m adding roughly one tonne of carbon per hectare per year. That’s a big win for soil structure, biology, and long-term fertility.
But there’s a catch. For every tonne of carbon stored, about 100 kg of nitrogen gets tied up—because carbon to nitrogen ratio is about 10:1. That’s nitrogen that doesn’t go into the crop, at least not right away. It’s a good sign environmentally (less leaching), but it forces us to think differently: we’re not just growing a crop above ground — we’re also feeding the soil. And both require nutrients.”
Managing Fields and Staying Flexible
Simon reflects:
“No two fields are ever the same. One of my best lessons has been to stay flexible — don’t do anything out of habit. For example, I never drill straight up and down the slope anymore. In one field, I direct-drilled linseed straight after the previous crop, no cultivation. Most fields still get a roll or a harrow to cover the seed, but only when needed.
Gypsum? I applied 4 tonnes per acre, three times over eight years. The results? Minimal. The Albrecht soil tests showed no real change, and when you do the chemical maths, you’d need unfeasible amounts to really shift the needle. Direct drilling — now that showed results. That’s what made the difference.”
Surprising Soil Behaviour
“One thing that constantly surprises me is how the soil handles moisture. When it’s dry, it goes rock hard. But once it wets up—even a little—it becomes crumbly and friable. That resilience has improved massively since adopting no-till.
In one field, I remember ploughing up an old meadow and seeing just two inches of dark topsoil over clay. The plough buried all the goodness. That was a turning point. Twenty years later, I believe I’ve rebuilt that topsoil layer—just through direct drilling and patience. It’s a stark contrast to where I started.”
Nitrogen, Legumes, and Root Systems
“There’s no denying it: crop yield still relates closely to the nitrogen you apply. Yes, legumes help. But the better the crop above ground, the better the root system—and that means better soil structure, more exudates, and more microbial activity. It’s a feedback loop.”
Straw and Worms: A Change Over Time
“For 15 years, I chopped and returned every bit of straw. The worms loved it at first. But more recently, it’s been sitting on the surface all winter, forming a mat that small seeds like linseed can’t get through. Now, I bale most of it. I’ve realised: the soil doesn’t need more carbon—it needs nitrogen to break down what’s already there.”
Rotations and Crop Choices
“Rotations? They’re always changing. I try to keep about 50% in wheat, with some barley, linseed, beans, and lucerne. About a third of the farm is spring-cropped. I treat each field on its own merits and decide what’s best for it next—nothing is fixed.”
Drainage, Moles, and Water Holding
“Drainage remains a challenge. I’ve started doing some moling to improve water movement. Last winter killed most of the wheat due to waterlogging. Mole drains helped, but only in the mole line—the soil in between takes years to catch up. So I cross-moled with a tine as an experiment.
On some fields, I now get lovely crumbly tilth after winter even with no plant cover, just from natural wetting and drying. But I still wonder: is my soil becoming hydrophobic, in a good way? That is, allowing water to drain through rather than sealing up. That’s the goal—especially on clay.”
Sheep and Grazing in Rotation
“Sheep are a handy tool, especially for cover crops and herbal leys. But I’ve learned to be very cautious—they can damage soil structure quickly, especially in wet weather. Just one day too long, and the field can end up full of holes that hold water into spring.”
Plough Trials
Despite the benefits min till has produced on his farm, Simon is beginning to experiment with ploughing this year to see whether it is possible to mineralise some of the nutrients within the soil. There are two trials going on, one looking at autumn ploughing and other, spring ploughing. He explains:
“The trial with autumn ploughing started in September. It was too dry and hard to plough at first so only a proportion of the field was ploughed. The other half of the field was direct drilled in October when the weather came good, and was no problem. On the ploughed side, I had to wait another two weeks to get on the land as it held all of the water. Although it is an interesting trial, it is going to be difficult to compare due to the delay in drilling the ploughed side. Establishment has been less good on the side which was ploughed compared to the direct drilled.”
The trial confirmed what Simon had been thinking: for his land, direct drilling is the way forward.
“It’s made my soil ploughable again.”
Undeterred, a second ploughing trial has been underway this spring, where a field was ploughed, power harrowed and rolled and then drilled two weeks later. Simon has been impressed with how the field has performed so far. The next door field has been direct drilled, so it will provide a good comparison to look at performance through this season to see how they grow!
“We’ve proved that we can build organic matter through our system, we are now looking at how we can balance occasional disturbance. I’ve been against it in the past because of protecting the soil structure that I have built up and not wanting to lose it, but I’m hoping that because it was in a good state before, it will recover quickly and be back to how it was before.”
I’ve done all the biological products, the trials, the tweaking. In the beginning, you throw everything at the problem. Over time, you start asking: what actually made the difference? I’ve spent years building organic matter. Now it’s time to start using it.
Many thanks to Simon for an inspirational walk and for sharing his knowledge so freely; it gave everyone lots to think about on the drive home!











































Recent Comments