
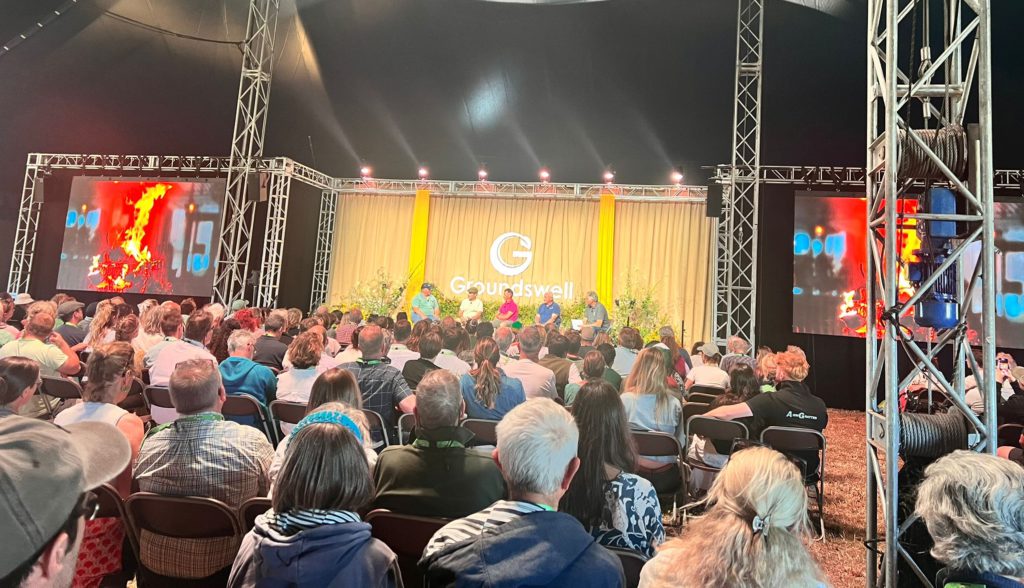
The final Farm Net Zero conference took place on 20th November 2025 at the Royal Cornwall Showground—under a blanket of unexpected snow!
Yet despite the weather, the room was full. Farmers, growers, advisors, researchers, community partners and supporters all gathered to reflect on five years of hard work, collaboration and learning. It felt less like the end of a project and more like the celebration of a community that has quietly reshaped what climate action looks like on real farms.
There was a striking range of delegates in the room. Young and older farmers and growers, a pretty even gender balance, and people representing every part of the agricultural community. But what really stood out was that every presenter brought a different perspective, a unique set of skills and lived experience, and together they created a strong thread of community that ran throughout the entire day. It was genuinely inspirational.
Farm Net Zero is a collaborative five-year project led by Duchy College Rural Business School, working in partnership with Farm Carbon Toolkit, Westcountry Rivers Trust, Soil Association, Innovative Farmers, Innovation for Agriculture, and Just Farmers. This ambitious initiative has been made possible thanks to funding from the National Lottery Community Fund. The final conference was organised by Duchy College with support from the FNZ project partners, to share some of the learnings, hear from participants, and to celebrate five years of the project.
A day rooted in practical progress
The day began with one of the FNZ Demonstration farmers, Mike Roberts of Blable Farm, who shared how he has changed farming practice to build greater business resilience. His reflections set the tone for the whole event: grounded, honest and focused on what works in the real world. Mike expressed heartfelt thanks to the project team at Duchy College, Farm Carbon Toolkit, Westcountry Rivers Trust, Innovative Farmers, Innovation for Agriculture and Just Farmers — a partnership that has been the backbone of Farm Net Zero since day one.
We then heard from Anthony Ellis of Pensipple Farm, who spoke about the trials he has been undertaking to reduce insecticide and fungicide use. By improving soil health, he has been able to cut fuel use for fieldwork by 10–15%—a meaningful saving both economically and environmentally. During this session, an important point was raised about the “elephant in the room”: who owns the carbon and wider natural capital benefits in a tenanted farming context? It’s an issue that will matter more and more as low-carbon farming evolves.
Malcolm Barrett of Tregooden Farm also reflected on the changes they have made on the farm. Through FNZ, the Barretts have reduced costs significantly by lowering inputs and outwintering cattle, with the biggest gains seen on arable fields—soil organic matter is up by around 3%, thanks to cover crops and min-till. Better soil health has reduced fuel use and enabled them to cut pesticide use, too.
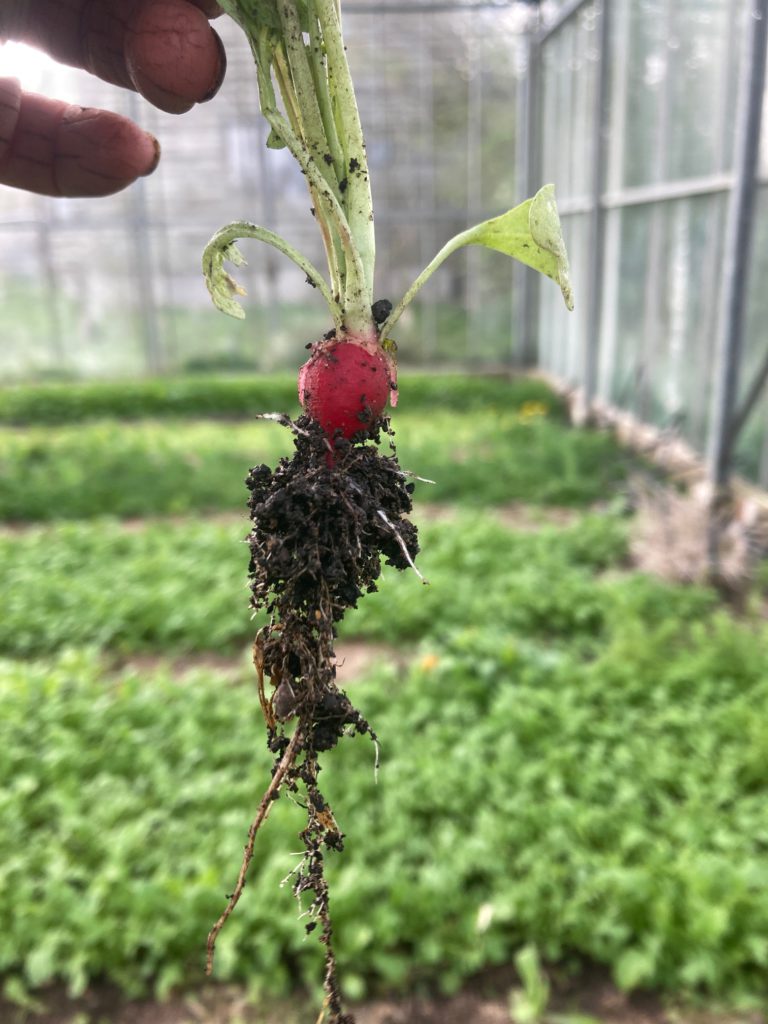
Amelia Lake from the Real Food Garden offered a shout-out to FCT for helping them understand their soils and how best to improve them. Their focus on no-dig systems and continuous compost additions has boosted soil health, and they’ve seen improvements in veg nutrient content, something they believe is closely linked to better soil function.
Nicola and Chris from Heligan Gardens shared how transformational their compost-focused Farm Net Zero field lab has been for their waste management system. By learning how to optimise composting, combining three separate waste streams while ensuring pathogen kill, they have been able to reduce waste, improve soil health and close nutrient loops more effectively.
We also heard from Emma Restorick at the Prideaux Walled Garden, who has been trialling ways to tackle bindweed and reduce carbon footprints through optimised home-grown compost and other nature-friendly techniques. Her work highlights just how adaptable and innovative small horticultural enterprises can be when given structured support and the space to experiment.
Robust data from real farms
The results of the project speak for themselves.
Over the course of the project, the project team carried out an extraordinary amount of monitoring and testing, including digging over 1,935 holes (over 10,000 auger dibs), and soil sampling 215 fields in both 2021 and 2025. This has created one of the richest long-term datasets of any UK farming climate project.
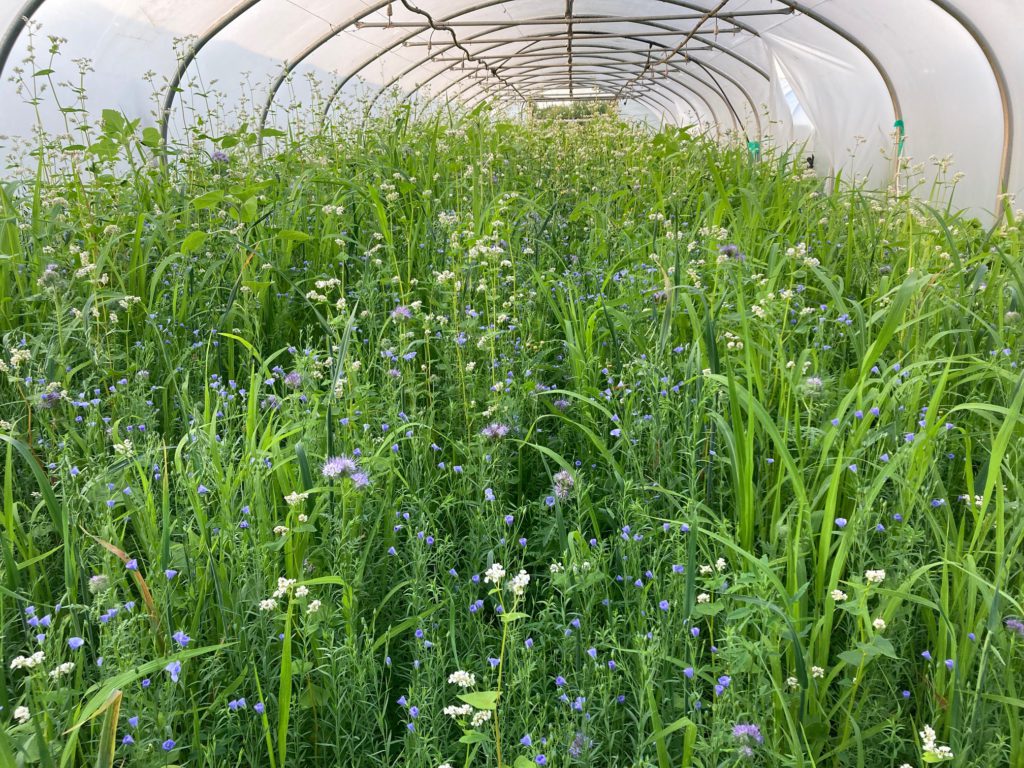
Initial findings show that fields in herbal leys in 2021 and still in herbal leys today sequestered an average of 3.35 tonnes of carbon per hectare per year. Across the project area, herbal ley coverage has increased by nearly 500 hectares, contributing significantly to soil carbon gains.
Habitat-based sequestration also shows clear gains: project farms collectively sequestered an additional 2,640 tCO₂e into on-farm habitats, supported by increases in both hedgerows and woodland. Hedgerow length increased from 607 km in Year 1 to 664 km in Year 5, with associated carbon sequestration rising from –2,338 tCO₂e to –2,854 tCO₂e. Farmers also planted 1,104 additional trees over the project period, reinforcing long-term carbon storage and biodiversity benefits.
Looking at changes in overall farm carbon footprints, every farming system involved in the project saw reductions:
- Horticulture: 4.3 tCO₂e → –7.54 tCO₂e
- Arable: 572.22 tCO₂e → 402.49 tCO₂e
- Beef & Sheep: 508.37 tCO₂e → 489.09 tCO₂e
- Dairy: 1.25 kg CO₂e/kg FPCM → 0.99
These improvements were largely driven by reductions in input use, particularly feed, fertiliser and fuel, supported by more diverse rotations, improved grazing management, better composting systems and healthier soils.
These were not theoretical models or one-off trials; these were whole-farm shifts, supported by careful measurement and farmer-led experimentation.

Last words
Finally, dairy farmer Andrew Brewer of Ennis Barton highlighted how evidence from Farm Net Zero had given him the confidence to encourage Arla to support farmers in growing herbal leys. As a member of Arla’s Sustainability Working Group his takeaway was powerful:
“The integrity and nutrient quality of food starts with farmers and growers.”
What came across loud and clear at the conference was the importance of steadfast and consistent activity, and the power of farmer-to-farmer learning. The project has built a community of farmers and advisers who have been willing to share their successes and failures openly, and this spirit of collaboration has been central to the project’s achievements.
What really made Farm Net Zero work
Beyond the numbers, what came through again and again was the strength of the community that has grown around the project. Demonstration farmers, monitor farms, advisers, researchers, gardeners, and local organisations, all willing to share what worked and what didn’t.
It powerfully demonstrates that progress doesn’t come from one-off interventions. It comes from steadfast, consistent activity—and from supporting farmers to try new things with confidence.
Farmers spoke freely about reducing inputs, changing rotations, experimenting with cover crops, improving composting systems, tackling weeds, integrating livestock, and rethinking their relationship with soil. The willingness to compare notes, challenges, successes and missteps has made this one of the most practical and trusted climate-action projects in UK farming.
So, what next?
This is the question many people asked during and after the conference. Farm Net Zero has clearly delivered:
- measurable reductions in emissions
- better soil health
- stronger business resilience
- increased biodiversity and more protective infrastructure (hedges, trees)
- greater collaboration across Cornwall’s food and farming community
- a five-year dataset that is rare at national level
The challenge now is to build on this success, not let it fade as the formal project period ends. Here are some priorities:
1. Share the learning more widely
The results, stories and practical guidance from Farm Net Zero need to reach a far larger audience — in Cornwall and beyond. Farmers elsewhere in the UK face similar challenges, and the FNZ experience can offer a roadmap: low-cost changes, peer-to-peer learning, and practical ways to reduce emissions while improving profitability. There’s a responsibility to translate these findings into accessible guidance, workshops, case studies and tools that any farmer can use.
2. Keep the community alive
The strength of FNZ was the trust between participants. Maintaining that network through events, field labs, farm walks, online spaces and continued collaboration will be vital. Farmers expressed a clear desire to keep learning from one another.
The good news is that some field labs and events will continue over the next few months, and the appetite for ongoing collaboration is strong.
3. Use the data to inform policy and practice
With more than 10,000 soil samples, detailed farm footprints and hundreds of farmer-led trials, FNZ now represents one of the richest real-world datasets on low-carbon farming in the UK.
That evidence can help shape better support schemes, more targeted advice, and more practical pathways for farmers transitioning towards net zero.
A beginning, not the end
Through the Farm Net Zero partnership, we’re committed to ensuring these insights don’t sit on a shelf. The findings from this project can play an important role in influencing how the sector and policymakers think about resilience, emissions reduction, soil health and resource efficiency.
As the conference was wrapped up, there felt a feeling of pride — not only in what’s been achieved, but in how it was achieved. Farmer-led, data-driven and grounded in real practice. Farm Net Zero has shown what’s possible when farmers are trusted, support experimentation, and commit to long-term learning rather than short-term initiatives.
The project will look forward to sharing the full results in early 2026 and helping ensure that the legacy of Farm Net Zero continues to grow. Cornwall has shown what can be done. Now the task is to help others follow.
We would like to extend our gratitude to the National Lottery Community Fund for their support throughout this five-year journey, and to all the farmers and partners who have made this work possible
































Recent Comments